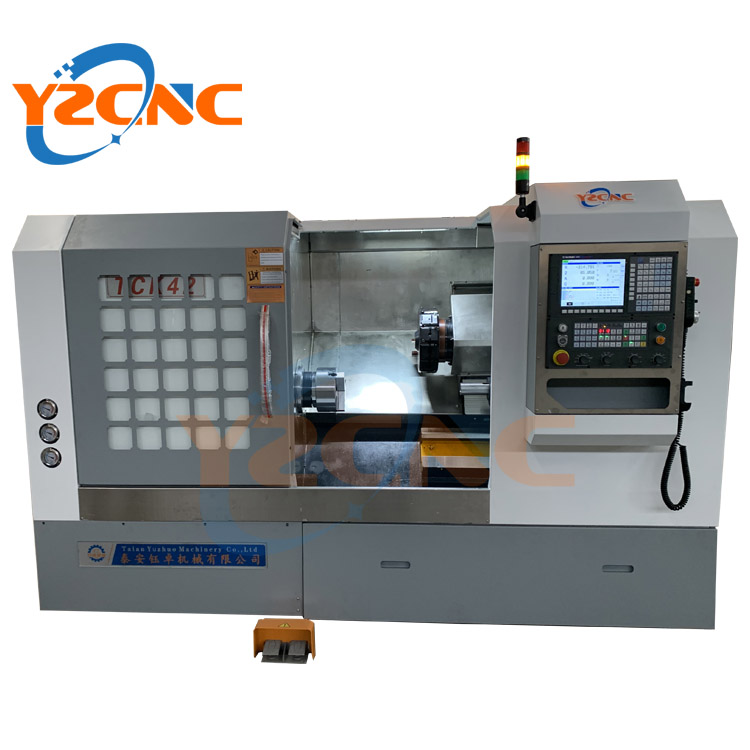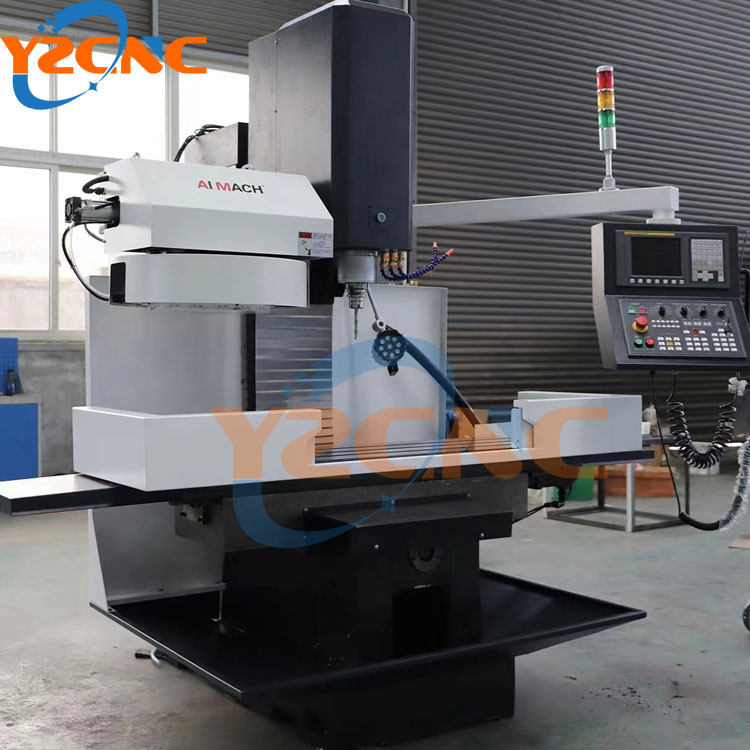
- VMC Series Vertical Machining Center
- VTC Series Vertical CNC Lathe Machine
- TCK Series Slant Bed CNC Lathe
- WRC Series Wheel Repair CNC Lathe
- QK Series Large Bore Pipe Thread Lathe
- CK Series Horizontal CNC Lathe Machine
- CK Series Heavy Duty CNC Lathe
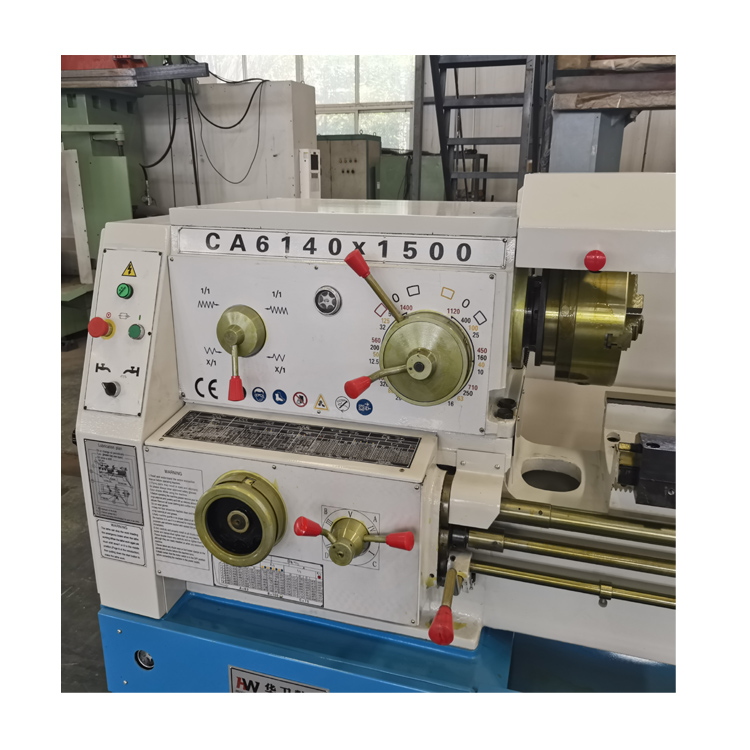
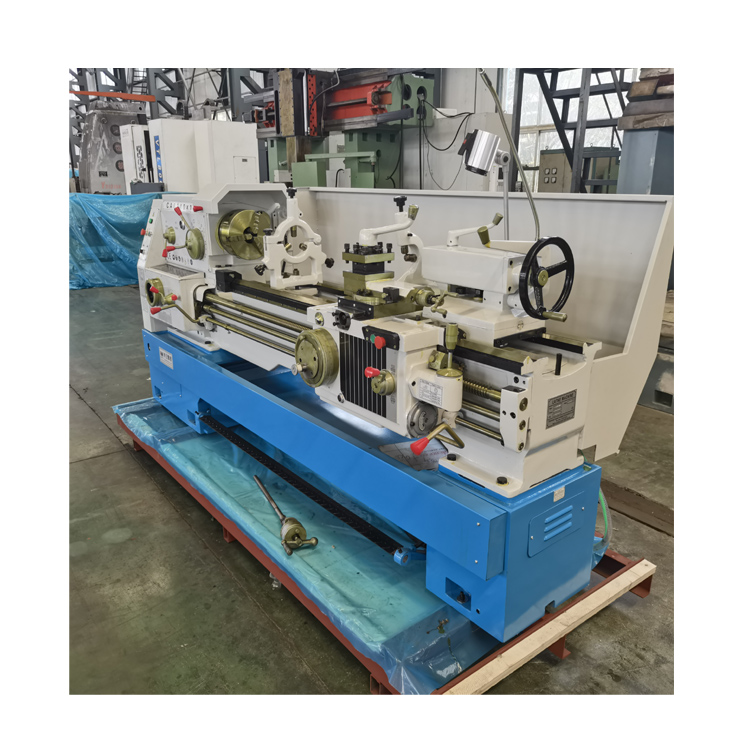
- CA Series Universal Lathe
- Drilling and Milling Machine
- Sawing Machine
- Slotting Machine and Shape
- Radial Drilling Machine
GET A QUICK REQUESTS
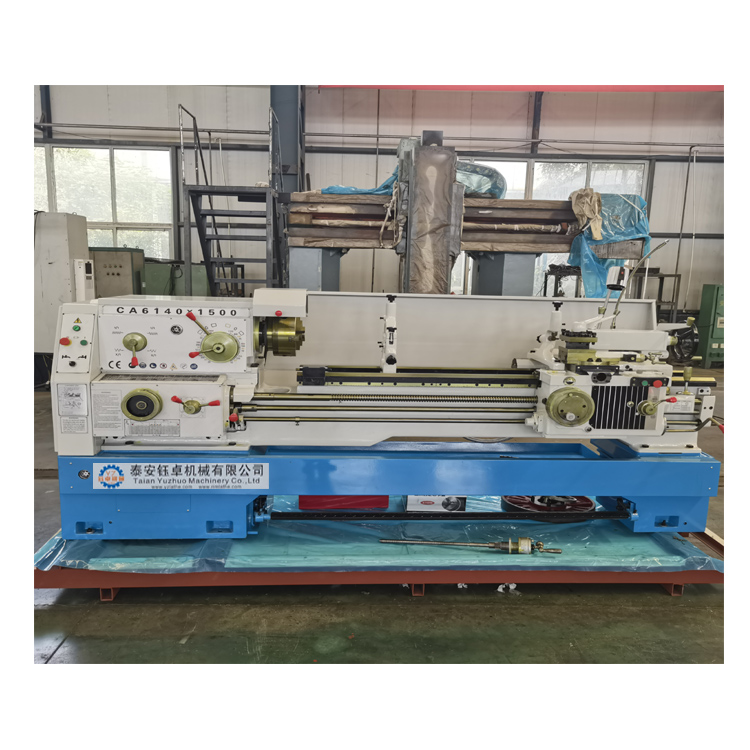 CA6240 Manual lathe, also known as a metalworking lathe, is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece on its axis to perform various operations, such as cutting, drilling, turning, facing, threading, and more. It is a fundamental tool in the metalworking industry and has been in use for centuries, providing precision and accuracy in shaping metal parts
CA6240 Manual lathe, also known as a metalworking lathe, is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece on its axis to perform various operations, such as cutting, drilling, turning, facing, threading, and more. It is a fundamental tool in the metalworking industry and has been in use for centuries, providing precision and accuracy in shaping metal parts
CA6240 Manual Lathe Specification
| CA Manual lathe CA62 gap lathe | ||||||
| ITM | UNIT | CA6140 CA6240 | CA6150 CA6250 | CA6161 CA6261 | CA6166 CA6266 | CA6180 CA6280 |
| Max.swing over bed | mm | 400 | 500 | 610 | 660 | 800 |
| Max.swing over carriage | mm | 210 | 300 | 370 | 400 | 540 |
| Max.swing in gap | mm | 630 | 720 | 830 | 880 | 1020 |
| Max.swing length | mm | 210 | 210 | 210 | 210 | 210 |
| Effective gap length | mm | 750/1000/1500/2000/3000/4000 | ||||
| Width of lathe bed | mm | 400 | ||||
| Section of turning tool | mm | 25*25 | ||||
| Spindle speed | rpm | 16-1400 (24steps) | ||||
| Spindle bore | mm | 52/80/105 | ||||
| Spindle nose | 52bore: ISO(GB)C6 (80/105 bore:D8) | |||||
| Spindle taper | 52Bore:No.6 MT6 ,80Bore: 1:20 105Bore: 1:20 | |||||
| No.of feed | 64kinds | |||||
| Range of metric threads | mm | 1-192mm 44 kinds | ||||
| Range of inch threads | tpi | 1-24tpi 21kinds | ||||
| Range of module threads | 0.25-48module 39kinds | |||||
| Range of diametral threads | DP | 1-96DP 37kinds | ||||
| Max.tailstock travel | mm | 150mm | ||||
| Tailstock Diameter | mm | 75mm | ||||
| Taper of tailstock hole | MT5 | |||||
| Main motor | kw | 7.5 10HP | ||||
Features of a Manual Lathe
A manual lathe consists of several components that work together to achieve the desired results. These components include:
Bed: The bed is the base of the lathe and provides a stable platform for the other components. It is usually made of cast iron or steel and has a flat and horizontal surface.
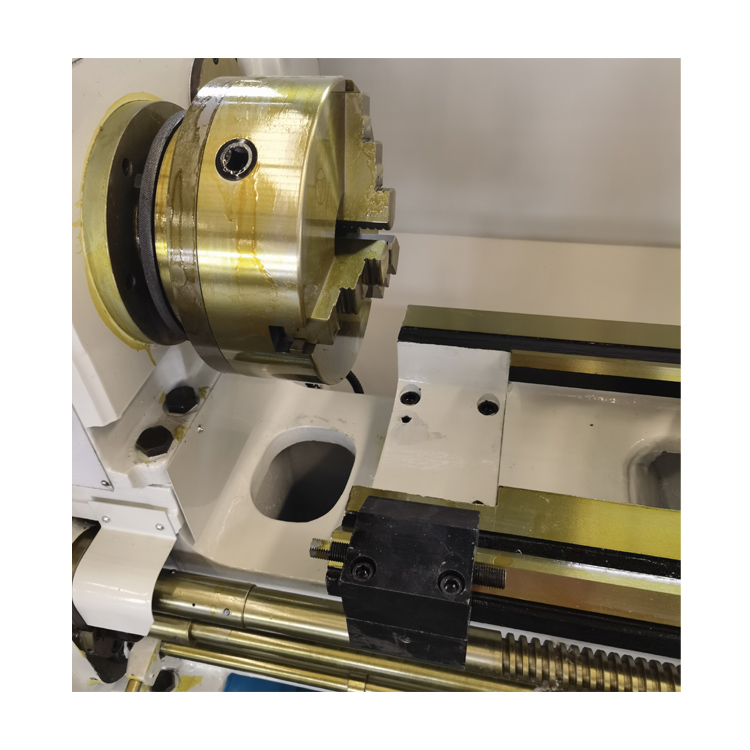 Headstock: The headstock is mounted on the bed and houses the main spindle, which rotates the workpiece. It also includes gears for controlling the spindle speed and a chuck for holding the workpiece.
Headstock: The headstock is mounted on the bed and houses the main spindle, which rotates the workpiece. It also includes gears for controlling the spindle speed and a chuck for holding the workpiece.
Tailstock: The tailstock is located at the opposite end of the bed from the headstock and includes a movable spindle that can be adjusted to support the other end of the workpiece.
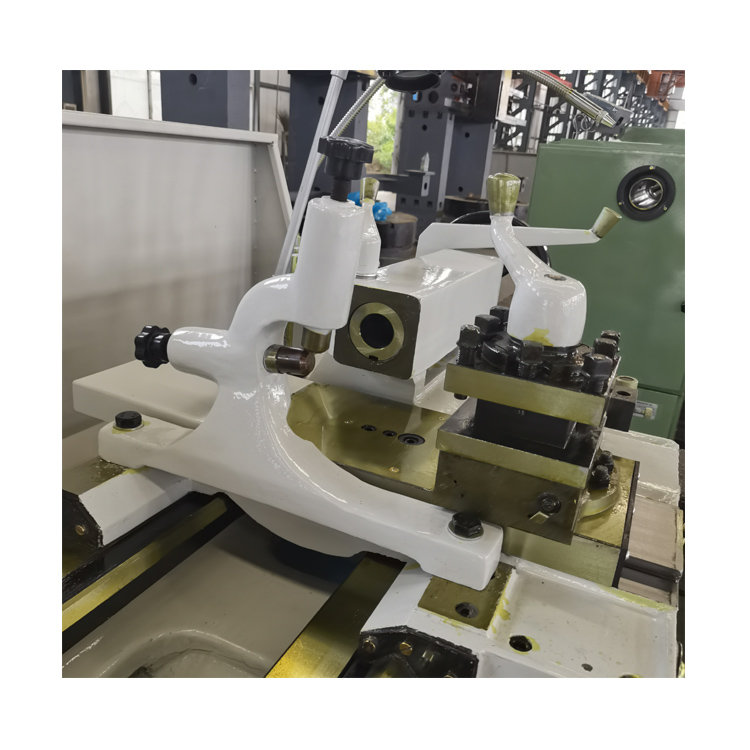
Carriage: The carriage is mounted on the bed and moves along the bed’s ways. It includes the cutting tool and can be moved manually to make various cuts on the workpiece.
Cross-slide: The cross-slide is mounted on the carriage and moves perpendicular to the bed’s ways. It provides the ability to make precise cuts and measurements.
Toolpost: The toolpost holds the cutting tool and can be adjusted to change the angle and position of the tool.
Feed rod: The feed rod is used to move the carriage and cross-slide in a precise and controlled manner.
Lead screw: The lead screw is used to move the carriage and cross-slide automatically to create threads on the workpiece.
Characteristics of a Manual Lathe
Manual lathes have several characteristics that make them unique compared to other machine tools. These include:
Precision: Manual lathe provide high precision and accuracy in shaping metal parts, making them ideal for applications that require tight tolerances.
Versatility: Manual lathe can perform a wide range of operations, including cutting, drilling, turning, facing, threading, and more.
Control: Manual lathe require a high level of operator skill and control to achieve the desired results. Operators must be able to adjust the cutting tool’s angle and position, control the spindle speed, and move the carriage and cross-slide in a precise and controlled manner.
Durability: Manual lathe are built to last and can withstand heavy use and abuse in industrial settings.
Cost-effectiveness: Manual lathe are often less expensive than other types of machine tools, making them an attractive option for small businesses and hobbyists.
Applications of a Manual Lathe
Manual lathe are used in a variety of applications across different industries, including:
Manufacturing: Manual lathe are used to produce a wide range of metal parts, including shafts, gears, valves, bearings, and more.
Repair and maintenance: Manual lathe are used to repair and maintain existing parts, such as worn-out bearings, damaged shafts, and broken gears.
Hobby and DIY: Manual lathes are popular among hobbyists and DIY enthusiasts who enjoy metalworking and want to create their own parts and tools.
Conclusion of Manual Lathe
Manual lathe are a fundamental tool in the metalworking industry and provide precision, accuracy, and versatility in shaping metal parts. They require a high level of operator skill and control but offer a cost-effective and durable solution for
Related Products














